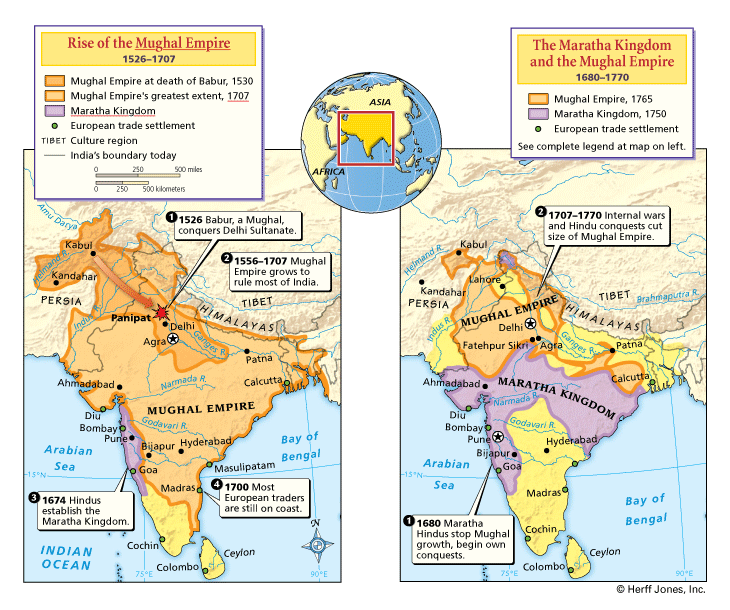
The Mughals were from Afghanistan and were descended from Tamerlane and Genghis Khan. They conquered most of India. Although they were Muslim, the Mughal emperors (shahs) were usually tolerant of other religions. The most famous monument of Mughal era is the Taj Mahal in Agra, the tomb of Mumtaz Mahal who was the favorite wife of Shah Jahan.
The Marathas continued to expand across India until 1761when they suffered a severe defeat against an Afghan and Mughal alliance. After 1761, the central government of the empire turned over much of its authority to local princes. Despite intense, sometimes violent, rivalry, the Maratha princes were not as easily manipulated by the Europeans as the Mughal nawabs. The Maratha Kingdom continued to be the dominant native power in India until 1818.
Aurangzeb conquered almost all of the remaining regions of India, bringing the empire to its greatest territorial extent. However, Aurangzeb re-introduced the jizyah, the traditional Muslim tax on non-Muslims, that earlier emperors had ignored. He also introduced rules restricting the non-Muslims in the government. Hindus and Sikhs rebelled against these policies, most importantly on the western coast.